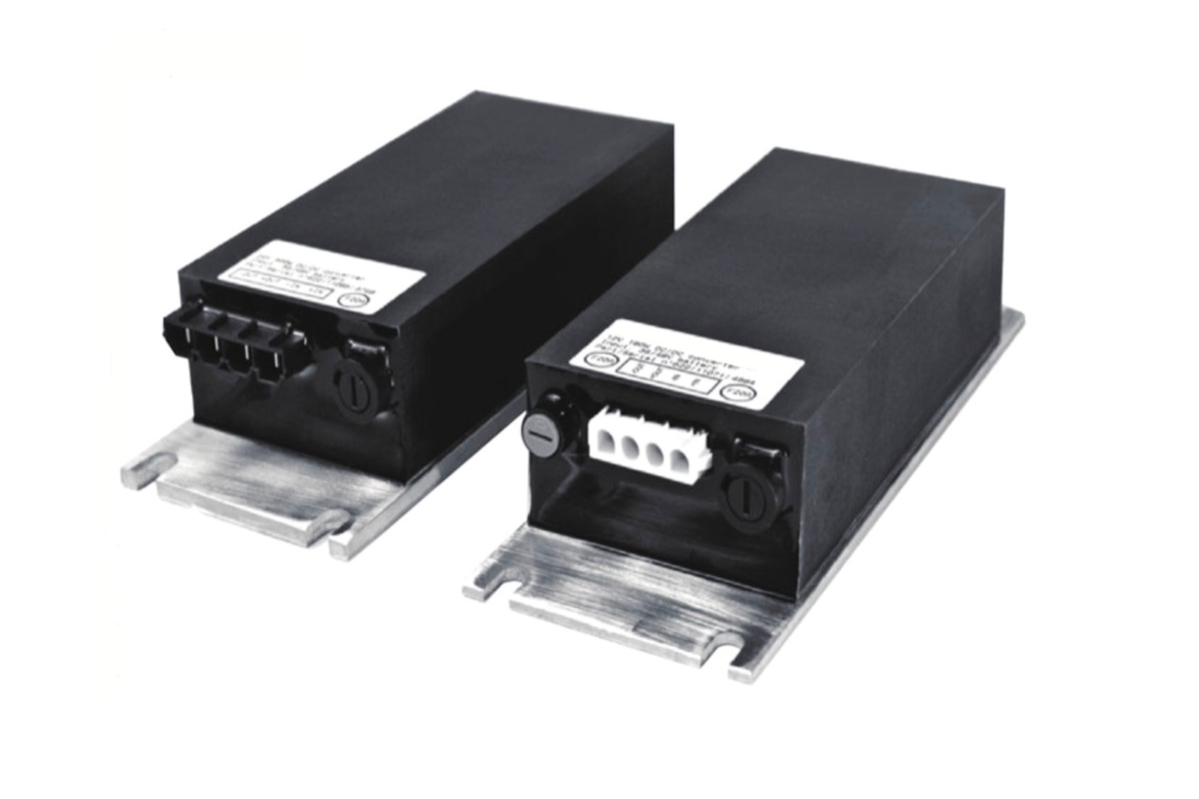
On many electric utility vehicles or LSVs equipped with 6-volt batteries, whether 36 or 48-volt vehicles, you will find that two of the batteries are "tapped" to achieve a 12-volt power source for headlights, tail lights, stereo systems or other accessories. While this can provide a convenient and economical source for the 12 volts of power needed, it can also have detrimental effects on your long-term battery life.
The real problem begins when it's time to recharge your battery pack. Keeping in mind that you have all your batteries connected in series, and now if you have operated your 12-volt accessories, you will have two batteries that are discharged more than the rest of your battery pack. When you begin to recharge the pack, one of two things can occur:
- The two "tapped" batteries will never catch up to the other batteries in the pack because they have been discharged more; or
- The rest of the pack may be overcharged as a result of the charger trying to bring the two "tapped" batteries to full capacity.
The continual undercharging or overcharging of any battery will have a negative effect on the lifespan and capacity of your battery pack. The concept of the converter is that no individual batteries in the pack are tapped at all. This spreads the additional loads of accessories evenly among all batteries and all cells, so discharge and recharge will be even and equal.
With the cost of batteries for the average electric vehicle being what it is, it is well worth the investment of a DC-DC Converter which can be purchased at just a fraction of what you will spend on new batteries. If you have purchased a vehicle from us in the last couple of years, they come equipped with a DC-DC Converter standard or require that one be added if you add additional electrical accessories.